Introducing the cellular respiration crossword puzzle answer key PDF, an indispensable resource for delving into the intricate processes that fuel life. This comprehensive guide empowers students and educators alike to unravel the complexities of cellular respiration, providing a clear understanding of its key steps and significance.
From the fundamental concepts of glycolysis to the intricate workings of the electron transport chain, this answer key serves as an invaluable tool for solidifying knowledge and enhancing comprehension.
Cellular Respiration Overview

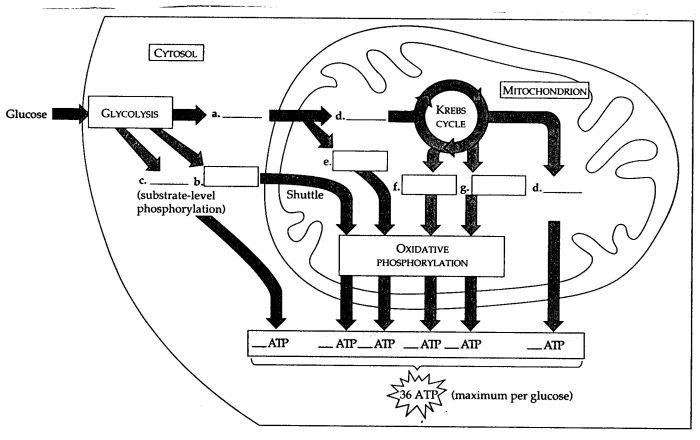
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells convert chemical energy stored in glucose into ATP, the main energy currency of the cell. It is a complex process that involves multiple steps, including glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain.
Key Steps in Cellular Respiration, Cellular respiration crossword puzzle answer key pdf
- Glycolysis:The first step in cellular respiration, glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm and breaks down glucose into two pyruvate molecules.
- Citric Acid Cycle:Also known as the Krebs cycle, this step occurs in the mitochondria and generates NADH and FADH2, which carry high-energy electrons.
- Electron Transport Chain:The final step, the electron transport chain is located in the inner mitochondrial membrane and uses the energy from NADH and FADH2 to generate ATP through oxidative phosphorylation.
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the first step in cellular respiration and takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. It breaks down glucose into two pyruvate molecules, releasing energy in the form of ATP and NADH.
Reactants and Products of Glycolysis
- Reactants:Glucose
- Products:2 Pyruvate, 2 ATP, 2 NADH
Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle): Cellular Respiration Crossword Puzzle Answer Key Pdf
The citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle, occurs in the mitochondria and is responsible for generating NADH and FADH2, which are used to generate ATP in the electron transport chain.
Key Intermediates and Reactions
- Key Intermediates:Citrate, Isocitrate, Alpha-ketoglutarate
- Reactions:Oxidative reactions, Decarboxylation reactions
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
The electron transport chain is the final step in cellular respiration and is located in the inner mitochondrial membrane. It uses the energy from NADH and FADH2 to generate ATP through a series of redox reactions.
Role in Generating ATP
The electron transport chain generates ATP through oxidative phosphorylation, a process that uses the energy released from the electron transfer to pump protons across the mitochondrial membrane, creating a gradient that drives ATP synthesis.
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation is the process by which ATP is generated in the electron transport chain. It involves the movement of protons across the mitochondrial membrane, creating a gradient that drives the synthesis of ATP by ATP synthase.
Role of ATP Synthase
ATP synthase is an enzyme that uses the energy from the proton gradient to synthesize ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate.
Factors Affecting Cellular Respiration
Several factors can influence the rate of cellular respiration, including:
- Temperature:Higher temperatures increase the rate of respiration.
- Oxygen Availability:Respiration requires oxygen, and its availability can affect the rate of the process.
- Substrate Availability:The availability of glucose or other substrates for respiration can influence the rate.
- Hormonal Regulation:Hormones such as thyroid hormone can affect the rate of respiration.
Crossword Puzzle Answer Key
| Crossword Clue | Answer | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| First step in cellular respiration | Glycolysis | The process that breaks down glucose into pyruvate |
| Electron carrier in the electron transport chain | NADH | Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, which carries high-energy electrons |
| Mitochondrial structure where the citric acid cycle occurs | Mitochondrial matrix | The inner compartment of mitochondria where the cycle takes place |
Question Bank
What is the significance of glycolysis in cellular respiration?
Glycolysis serves as the initial step in cellular respiration, breaking down glucose to generate energy in the form of ATP.
How does the electron transport chain contribute to ATP production?
The electron transport chain utilizes the energy released from electron transfer to pump protons across a membrane, creating a gradient that drives ATP synthesis.
What factors can influence the rate of cellular respiration?
Factors such as temperature, oxygen availability, and substrate concentration can affect the rate of cellular respiration.