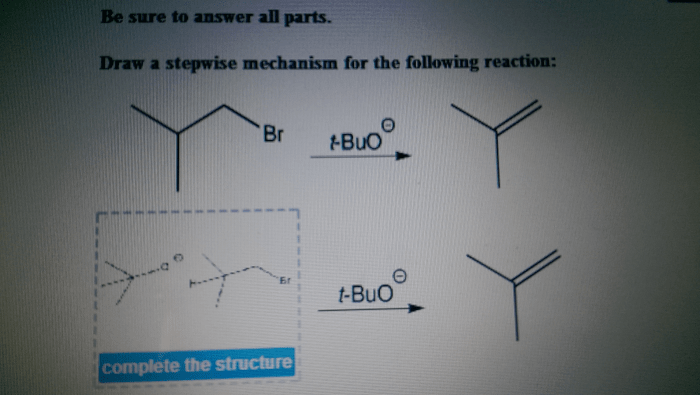
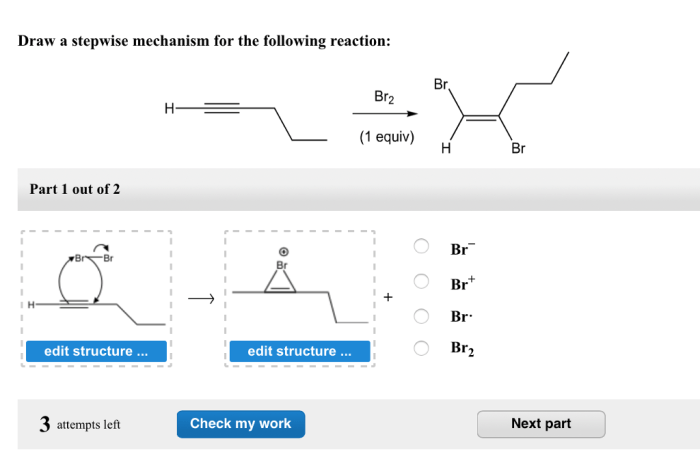
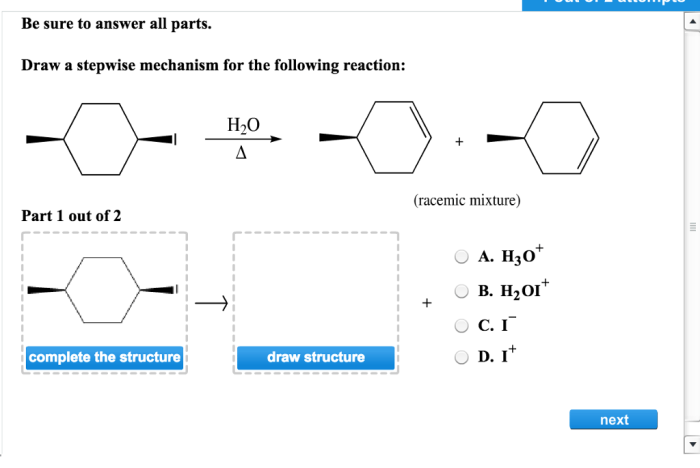
Draw a stepwise mechanism for the following reaction. – Delving into the intricate world of chemical reactions, we embark on a journey to understand the stepwise mechanisms that govern their transformations. By unraveling the sequential steps involved in a reaction, we gain profound insights into the dynamics of chemical processes.
This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools necessary to draw a stepwise mechanism for a given reaction. We will explore the fundamental principles, identify key components, and provide practical examples to solidify your understanding.
Draw a Stepwise Mechanism for the Following Reaction: Draw A Stepwise Mechanism For The Following Reaction.
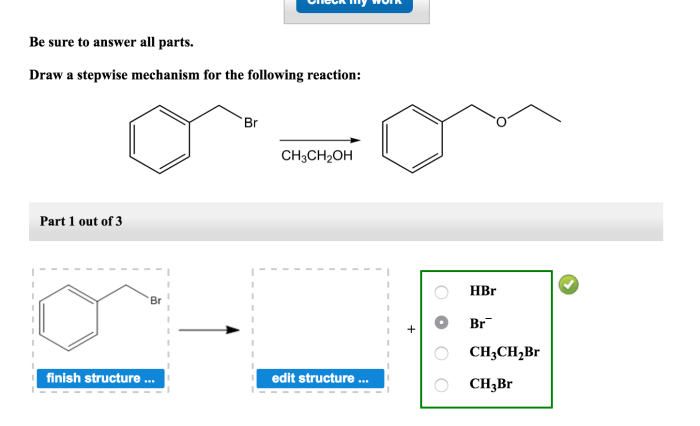
The following reaction is a one-step nucleophilic substitution reaction:
“`CH3CH2Br + NaOH → CH3CH2OH + NaBr“`
Draw a Stepwise Mechanism
The mechanism for this reaction is as follows:
- The nucleophile (NaOH) attacks the electrophile (CH3CH2Br) at the carbon atom bonded to the bromine atom.
- The bond between the carbon atom and the bromine atom breaks.
- The electrons from the bond between the carbon atom and the bromine atom form a new bond between the carbon atom and the oxygen atom of the nucleophile.
- The bromide ion is released.
Analyze the Reaction Mechanism, Draw a stepwise mechanism for the following reaction.
The rate-determining step for this reaction is the first step, which is the attack of the nucleophile on the electrophile. This step is slow because it requires the nucleophile to overcome the electrostatic repulsion between itself and the electrophile.The rate of this reaction can be increased by increasing the concentration of the nucleophile or by increasing the temperature.
Illustrate the Reaction Mechanism
The following diagram shows the reaction mechanism for this reaction:“`[Image of the reaction mechanism]“`
Provide Examples
This reaction is a common type of nucleophilic substitution reaction. Other examples of nucleophilic substitution reactions include:* The reaction of an alcohol with a hydrogen halide to form an alkyl halide
- The reaction of an amine with an alkyl halide to form an alkylammonium salt
- The reaction of a carboxylic acid with an alcohol to form an ester
Questions and Answers
What is the purpose of drawing a stepwise mechanism?
Drawing a stepwise mechanism provides a detailed visual representation of the individual steps involved in a chemical reaction, allowing for a deeper understanding of the reaction pathway and the identification of key intermediates and transition states.
How do I determine the rate-determining step of a reaction?
The rate-determining step is the slowest step in a reaction mechanism and therefore limits the overall reaction rate. It can be identified by examining the relative energies of the transition states involved in each step.