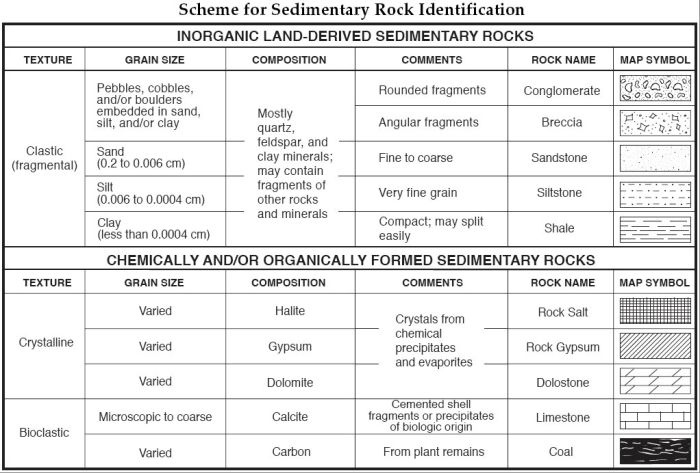
Embark on a journey into the realm of sedimentary rock identification with our comprehensive answer key, meticulously crafted to illuminate the significance and intricacies of this captivating field. Sedimentary rock identification lab answer key, an indispensable tool for geologists, engineers, and environmental scientists, unlocks the secrets of Earth’s history, revealing the processes that have shaped our planet over eons.
This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse types of sedimentary rocks, their formation processes, and the key characteristics that distinguish them. Through visual examination, petrographic analysis, and geochemical techniques, we empower you to decipher the language of these ancient rocks, unlocking their stories of depositional environments, provenance, and diagenetic history.
1. Sedimentary Rock Identification Lab
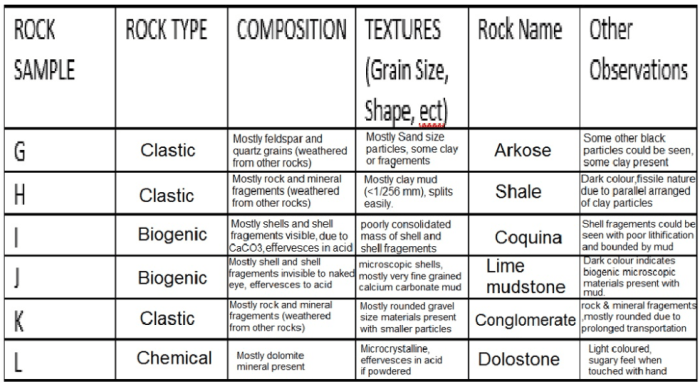
The Sedimentary Rock Identification Lab is designed to provide students with hands-on experience in identifying and classifying sedimentary rocks. The lab’s objectives are to:
- Familiarize students with the different types of sedimentary rocks and their formation processes.
- Develop students’ skills in using visual examination, petrographic analysis, and geochemical analysis to identify sedimentary rocks.
- Provide students with an understanding of the applications of sedimentary rock identification in various fields.
2. Key Characteristics of Sedimentary Rocks, Sedimentary rock identification lab answer key
Sedimentary rocks are formed from the accumulation and lithification of sediments. The type of sedimentary rock formed depends on the composition, texture, and grain size of the sediments. The key characteristics of sedimentary rocks include:
- Composition:Sedimentary rocks can be composed of a variety of materials, including minerals, organic matter, and rock fragments.
- Texture:The texture of a sedimentary rock refers to the size, shape, and arrangement of the grains that make up the rock.
- Grain size:The grain size of a sedimentary rock refers to the diameter of the individual grains that make up the rock.
- Sedimentary structures:Sedimentary structures are features that are formed during the deposition and lithification of sediments. These structures can provide clues to the environment in which the sediment was deposited.
3. Methods for Sedimentary Rock Identification
There are a variety of methods that can be used to identify sedimentary rocks. These methods include:
- Visual examination:Visual examination is the most basic method of sedimentary rock identification. It involves examining the rock’s color, texture, and grain size.
- Petrographic analysis:Petrographic analysis is a more detailed method of sedimentary rock identification. It involves examining the rock’s thin section under a microscope.
- Geochemical analysis:Geochemical analysis is a method of sedimentary rock identification that involves analyzing the rock’s chemical composition.
4. Interpretation of Sedimentary Rock Data
The results of sedimentary rock analysis can be used to interpret the depositional environment, provenance, and diagenetic history of the rock. Depositional environment refers to the environment in which the sediment was deposited. Provenance refers to the source of the sediment.
Diagenetic history refers to the changes that have occurred to the rock since it was deposited.
5. Applications of Sedimentary Rock Identification
Sedimentary rock identification has a wide range of applications in geology and Earth sciences, engineering and construction, and environmental science. In geology and Earth sciences, sedimentary rock identification is used to:
- Determine the age and depositional environment of sedimentary rocks.
- Reconstruct the geologic history of an area.
- Identify potential sources of groundwater and hydrocarbons.
Detailed FAQs: Sedimentary Rock Identification Lab Answer Key
What is the significance of sedimentary rock identification?
Sedimentary rock identification is crucial for understanding Earth’s history, reconstructing past environments, and assessing geological hazards. It also aids in mineral exploration, engineering projects, and environmental studies.
What are the key characteristics used to identify sedimentary rocks?
Grain size, texture, composition, and sedimentary structures are the primary characteristics used to distinguish between different types of sedimentary rocks.
What methods are employed for sedimentary rock identification?
Visual examination, petrographic analysis, and geochemical analysis are the common methods used for sedimentary rock identification.