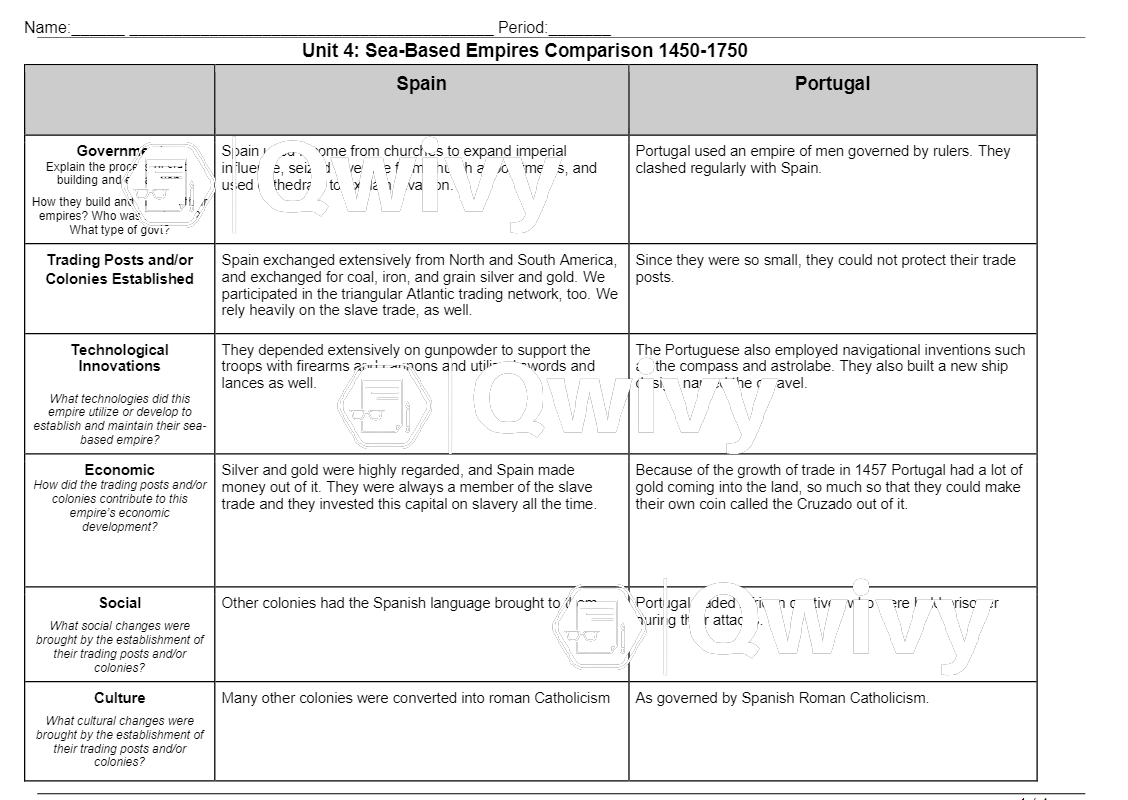
Unit 4 sea based empires comparison – In this comprehensive analysis, Unit 4: Sea-Based Empires: A Comparative Analysis, we embark on an authoritative exploration of the profound impact of sea-based empires on the course of human history. This comparative study delves into the defining characteristics, strengths, and legacies of these maritime powers, shedding light on their pivotal role in global exploration, trade, and cultural exchange.
Through a meticulous examination of their geography, political structures, economic activities, military capabilities, and cultural achievements, we uncover the unique contributions of these empires and their lasting influence on the development of naval warfare, maritime technology, and global affairs.
Introduction

Sea-based empires are political entities that exercise control over vast maritime territories, often through naval power and trade networks. Comparing sea-based empires provides valuable insights into the strategies, challenges, and legacies of these powerful entities that shaped global history.
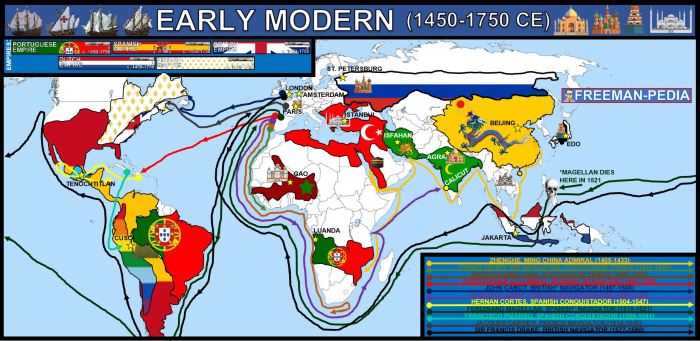
Throughout history, numerous sea-based empires have emerged, including the Phoenicians, Greeks, Romans, Arabs, Portuguese, Spanish, Dutch, British, and French. These empires played pivotal roles in exploration, trade, cultural exchange, and the spread of ideas.
Comparison of Sea-Based Empires

Sea-based empires, characterized by their maritime prowess and global reach, played a pivotal role in shaping world history. By comparing various aspects of these empires, we can gain insights into their similarities, differences, and contributions to civilization.
Geography
Sea-based empires were often established in strategic coastal regions with access to major sea routes. Their geographic locations allowed them to control maritime trade, expand their territories through naval conquests, and project power across vast distances.
| Empire | Geography |
|---|---|
| Phoenicia | Eastern Mediterranean coast, modern-day Lebanon |
| Carthage | North African coast, modern-day Tunisia |
| Greece | Aegean and Ionian Sea coasts |
| Rome | Mediterranean Sea coasts |
| Portugal | Atlantic Ocean coast, Iberian Peninsula |
| Spain | Mediterranean and Atlantic Ocean coasts, Iberian Peninsula |
| Netherlands | North Sea coast |
| England | North Sea and Atlantic Ocean coasts |
Case Studies
To provide a comprehensive analysis of sea-based empires, it is essential to delve into specific case studies that highlight their unique characteristics, strengths, and weaknesses. By examining the naval battles, trade routes, and cultural influences of these empires, we can gain a deeper understanding of their impact on global history.
Athenian Empire
The Athenian Empire emerged as a dominant maritime power in the 5th century BCE. Its strength lay in its formidable navy, which consisted of triremes, sleek and maneuverable warships. The Athenians relied on their naval prowess to establish control over the Aegean Sea and secure their trade routes.
They engaged in numerous naval battles, including the decisive Battle of Salamis in 480 BCE, which marked a turning point in the Greco-Persian Wars.
The Athenian Empire also played a significant role in trade and commerce. It established trade routes throughout the Mediterranean, connecting Greece with Egypt, Phoenicia, and other regions. The Athenians used their maritime dominance to control access to resources and markets, fostering economic prosperity and cultural exchange.
Carthaginian Empire, Unit 4 sea based empires comparison
The Carthaginian Empire, founded by Phoenician settlers in the 9th century BCE, became a formidable sea power in the western Mediterranean. Carthage possessed a large and well-equipped navy, which it used to expand its territories and establish trading networks. The Carthaginians were skilled shipbuilders and navigators, venturing as far as the Atlantic Ocean and establishing colonies in North Africa, Spain, and Sicily.
The Carthaginian Empire engaged in numerous naval battles with its rivals, including the Greeks and Romans. One of the most famous battles was the Battle of Zama in 202 BCE, where the Carthaginians were decisively defeated by the Romans, marking the end of the Carthaginian Empire.
Impact of Sea-Based Empires
Sea-based empires have played a profound role in shaping the course of global history. Their maritime dominance has enabled them to explore uncharted territories, establish vast trade networks, and facilitate cultural exchange on an unprecedented scale.
Exploration, Trade, and Cultural Exchange:
- Sea-based empires embarked on ambitious voyages of exploration, driven by a thirst for knowledge, wealth, and adventure. They discovered new continents, charted unknown seas, and established colonies in distant lands.
- These empires also fostered extensive trade networks that connected different parts of the world. They transported goods such as spices, textiles, and precious metals, leading to economic growth and cultural exchange.
- Cultural exchange flourished as sea-based empires interacted with diverse civilizations. Ideas, technologies, and artistic styles were disseminated, leading to a rich tapestry of cultural influences.
Naval Warfare and Maritime Technology:
- Sea-based empires invested heavily in developing powerful navies to protect their maritime interests. They constructed advanced ships, developed innovative naval tactics, and trained skilled sailors.
- The need for efficient navigation and communication led to advancements in maritime technology, including the invention of the compass, astrolabe, and improved shipbuilding techniques.
- These technological advancements not only enhanced naval warfare but also facilitated maritime exploration and trade, further expanding the reach of sea-based empires.
Legacy of Sea-Based Empires
The legacy of sea-based empires extends far beyond their territorial boundaries and historical existence. Their influence continues to shape contemporary global affairs, leaving lasting cultural, political, and economic imprints.
Cultural Legacies
Sea-based empires played a pivotal role in fostering cultural exchange and dissemination. They facilitated the spread of languages, religions, and artistic traditions across vast distances. For instance, the British Empire introduced English as a global lingua franca, while the Spanish Empire disseminated Catholicism throughout the Americas.
These cultural influences continue to resonate today, shaping global communication, religious practices, and artistic expression.
Political Legacies
The geopolitical order established by sea-based empires has had a profound impact on contemporary international relations. Colonial boundaries drawn by these empires often persist as national borders, influencing territorial disputes and regional alliances. Moreover, the concept of maritime sovereignty and territorial waters, established during the era of sea-based empires, remains a cornerstone of international law and maritime governance.
Economic Legacies
Sea-based empires were instrumental in establishing global trade networks and facilitating economic development. They created a system of interconnected markets, connecting different regions and stimulating economic growth. The infrastructure developed by these empires, such as ports, canals, and shipping routes, continues to facilitate global trade and economic exchange.
Expert Answers: Unit 4 Sea Based Empires Comparison
What are the defining characteristics of a sea-based empire?
Sea-based empires are maritime powers that rely on naval dominance to establish and maintain control over vast territories. They typically possess strong shipbuilding capabilities, skilled navigators, and powerful navies, enabling them to project their influence across oceans.
How did sea-based empires contribute to global exploration and trade?
Sea-based empires played a crucial role in expanding human knowledge of the world. Their expeditions and trade routes connected distant regions, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies. They established colonies and trading posts, which became hubs for economic and cultural exchange.
What was the impact of sea-based empires on naval warfare and maritime technology?
Sea-based empires were major drivers of innovation in naval warfare and maritime technology. They developed new ship designs, weapons systems, and navigation techniques. The rivalry among empires led to a continuous arms race, resulting in advancements in shipbuilding, weaponry, and naval tactics.
