Immigration myths and facts quiz – Dive into the world of immigration with our engaging quiz, where we’ll debunk common myths and uncover the truth. Get ready to challenge your assumptions and gain a deeper understanding of this complex issue.
In this quiz, we’ll explore the impact of immigration on the economy, society, and culture. We’ll also delve into the political and legal aspects of immigration, examining the ethical considerations that shape our policies and practices.
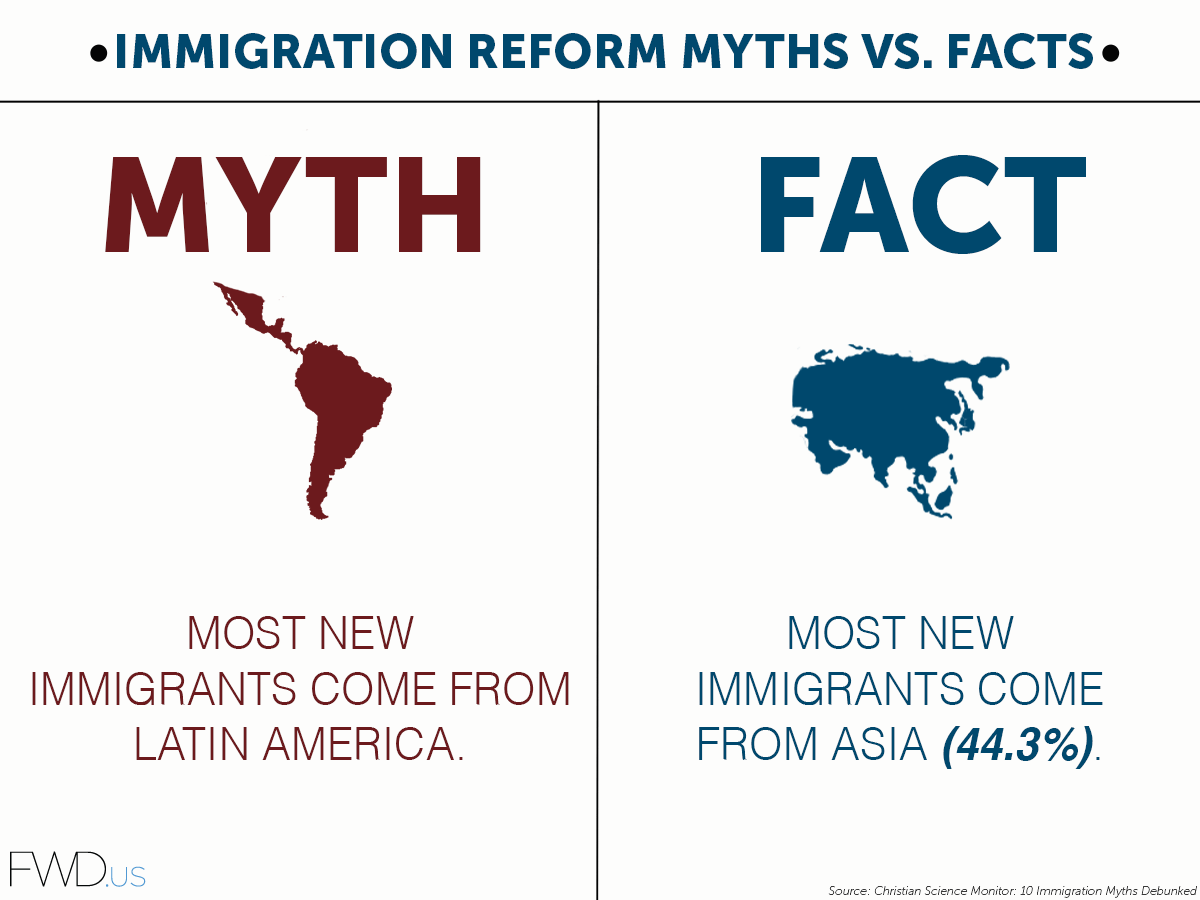
Immigration Myths vs. Facts
Many common misconceptions surround immigration. It’s crucial to separate facts from myths to form informed opinions.
Immigration Myths vs. Facts Table
The following table presents common immigration myths and their corresponding facts:
| Myth | Fact | Explanation | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Immigrants take jobs away from native-born workers. | Immigrants often create new jobs and contribute to economic growth. | Immigrants often fill labor shortages in industries facing a shortage of workers. | Cato Institute |
| Immigrants are a drain on the economy. | Immigrants pay taxes and contribute to the economy. | Immigrants contribute to Social Security and Medicare through their taxes. | Center on Budget and Policy Priorities |
| Immigrants commit more crimes than native-born citizens. | Immigrants are less likely to commit crimes than native-born citizens. | Studies have shown that immigrants are less likely to be arrested or incarcerated than native-born citizens. | Cato Institute |
| Immigrants don’t learn English. | Many immigrants learn English and become fluent. | Immigrants often take English classes and make an effort to integrate into American society. | Migration Policy Institute |
| Immigrants are all low-skilled workers. | Immigrants come from diverse backgrounds and skill levels. | Many immigrants are highly skilled workers who contribute to the economy in various fields. | American Immigration Council |
Impact of Immigration on the Economy
Immigration has significant economic implications, encompassing both positive and negative impacts. It is crucial to analyze these effects comprehensively to form an informed understanding of the complex relationship between immigration and economic outcomes.
On the one hand, immigration can stimulate economic growth by increasing the labor force, fostering innovation, and expanding consumer markets. Immigrants often bring valuable skills, knowledge, and entrepreneurial spirit, contributing to a more diverse and dynamic economy.
Positive Impacts
- Increased Labor Force:Immigrants can fill labor shortages in industries facing skill gaps, boosting productivity and output.
- Innovation and Entrepreneurship:Immigrants are more likely to start businesses and create jobs, contributing to economic diversification and technological advancement.
- Consumer Demand:Immigrants expand consumer markets by increasing demand for goods and services, stimulating economic growth.
On the other hand, immigration can also pose challenges, particularly in the short term. Increased competition for jobs and public resources can strain local communities.
Negative Impacts
- Competition for Jobs:In some sectors, immigrants may compete with native-born workers for jobs, potentially leading to lower wages or displacement.
- Strain on Public Resources:Immigrants can put a strain on public services such as education, healthcare, and housing, especially in areas with limited resources.
However, it is important to note that the overall economic impact of immigration is complex and varies depending on factors such as the skills and education of immigrants, the size and composition of the existing workforce, and the economic policies of the receiving country.
Social and Cultural Effects of Immigration

Immigration can have significant social and cultural effects on receiving countries. These effects can be both positive and negative, and they can vary depending on the specific circumstances of each country and the characteristics of the immigrant population.
One of the most visible effects of immigration is increased diversity. This can be a positive development, as it can lead to cultural exchange and new perspectives. Immigrants often bring with them new ideas, customs, and traditions, which can enrich the receiving country’s culture.
For example, the influx of immigrants from Mexico and other Latin American countries to the United States has led to a growing popularity of Spanish language and culture in the US.
Social Integration Challenges
However, increased diversity can also lead to challenges related to social integration. Immigrants may face language barriers, cultural differences, and discrimination, which can make it difficult for them to fully integrate into the receiving society. This can lead to social tensions and conflict.
Political and Legal Aspects of Immigration
Immigration policies vary widely around the world, influenced by factors such as economic needs, social values, and geopolitical considerations. Different types of policies include:
- Open immigration:Allows individuals to enter and reside in a country with minimal restrictions.
- Restricted immigration:Limits the number of immigrants allowed to enter, often based on quotas or specific criteria.
- Selective immigration:Prioritizes certain types of immigrants, such as skilled workers, refugees, or family members of citizens.
Legal Frameworks Governing Immigration
Immigration is governed by complex legal frameworks that establish rules for citizenship, asylum, and deportation.
Citizenship
- Birthright citizenship:Grants citizenship to individuals born within a country’s borders.
- Naturalization:Allows foreign-born individuals to become citizens through a process that typically involves meeting residency requirements and passing citizenship tests.
Asylum
- Refugee status:Recognizes individuals who have fled their home countries due to persecution or well-founded fear of persecution.
- Asylum seekers:Individuals who apply for refugee status and are awaiting a decision.
Deportation
- Grounds for deportation:Include violations of immigration laws, criminal convictions, or posing a security risk.
- Due process:Individuals facing deportation have the right to legal representation and fair hearings.
Political Debates Surrounding Immigration
Immigration is a highly politicized issue, with both pro-immigration and anti-immigration perspectives.
Pro-Immigration Perspectives
- Economic benefits:Immigrants contribute to the economy through labor, innovation, and entrepreneurship.
- Cultural diversity:Immigration brings new ideas, traditions, and perspectives, enriching society.
- Humanitarian concerns:Supporting refugees and asylum seekers is a moral obligation.
Anti-Immigration Perspectives
- Economic concerns:Immigrants may compete for jobs and resources, potentially lowering wages and straining social services.
- Cultural preservation:Immigration can lead to changes in cultural norms and values, which some view as a threat to national identity.
- Security concerns:Immigration can be seen as a potential source of terrorism or crime.
Ethical Considerations in Immigration: Immigration Myths And Facts Quiz
Immigration raises complex ethical dilemmas that challenge individuals, societies, and policymakers. Understanding these ethical implications is crucial for developing fair and just immigration policies.
One of the primary ethical concerns in immigration is the responsibility of receiving countries towards immigrants. This includes providing basic rights and protection from exploitation. Immigrants often face vulnerabilities and may be at risk of discrimination, abuse, and human trafficking.
Ethical considerations demand that receiving countries uphold the human rights of all individuals, regardless of their immigration status.
Responsibilities of Receiving Countries
- Provide basic human rights, including access to healthcare, education, and legal protection.
- Combat discrimination and promote social integration for immigrants.
- Address the needs of vulnerable immigrants, such as refugees, asylum seekers, and undocumented workers.
li>Prevent exploitation and human trafficking by strengthening labor laws and providing support services.
Another ethical dilemma in immigration is the tension between national sovereignty and the rights of individuals. Countries have the right to control their borders and regulate immigration. However, this right must be balanced against the moral obligation to provide refuge for those fleeing persecution or seeking a better life.
Balancing National Sovereignty and Individual Rights, Immigration myths and facts quiz
- Respect the rights of asylum seekers and refugees under international law.
- Avoid creating policies that lead to statelessness or indefinite detention.
- Consider the humanitarian impact of immigration policies on individuals and families.
- Promote dialogue and cooperation between countries to address global migration challenges.
Ethical considerations in immigration also extend to the individuals and societies involved. Immigrants may face moral dilemmas when deciding whether to leave their home countries, often driven by desperation or the desire for a better life. Societies, too, must grapple with the ethical implications of immigration on their social fabric and cultural identity.
Ethical Dilemmas for Individuals and Societies
- Individuals may face conflicts between loyalty to their home country and their new country.
- Societies must balance the preservation of their cultural heritage with the need for social cohesion and inclusivity.
- Immigration can raise questions about national identity and the rights of citizens versus non-citizens.
- It is essential to foster dialogue and understanding between immigrants and non-immigrants to promote mutual respect and cooperation.
In conclusion, ethical considerations in immigration require a nuanced and compassionate approach. By understanding the ethical implications of immigration policies and practices, we can work towards creating fair and just systems that uphold human rights, respect national sovereignty, and promote the well-being of both immigrants and receiving societies.
FAQ Guide
What is the difference between an immigrant and a migrant?
An immigrant is someone who has moved to a new country to live permanently, while a migrant is someone who moves from one place to another, often for a temporary period.
Is it true that immigrants take jobs away from native-born citizens?
Studies have shown that immigration has a positive impact on the economy, creating new jobs and boosting economic growth.
What are the main challenges faced by immigrants?
Immigrants often face challenges such as language barriers, cultural differences, discrimination, and lack of access to healthcare and education.
