X ray kvp and mas chart – X-ray KVP and MAS charts are indispensable tools for radiographers, enabling them to determine optimal exposure settings for clear and diagnostically valuable images. Join us as we delve into the intricacies of these charts, exploring their history, components, and practical applications.
Understanding the concepts of Kilovoltage Peak (KVP) and Milliampere Seconds (MAS) is crucial for manipulating image quality and minimizing patient exposure. This comprehensive guide will provide you with a thorough understanding of these parameters and their impact on X-ray imaging.
X-Ray KVP and MAS Chart Overview
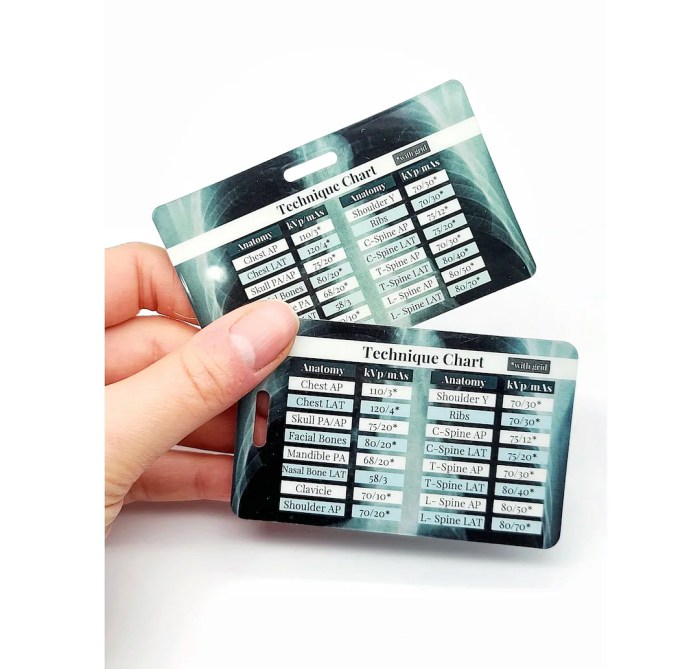

An X-ray KVP and MAS chart is an essential tool in radiology, providing guidance on the appropriate settings for X-ray imaging. It helps ensure optimal image quality and patient safety by specifying the correct kilovoltage peak (KVP) and milliampere-seconds (MAS) for a given examination.
History and Evolution
The first X-ray KVP and MAS charts were developed in the early 1900s, when X-ray technology was still in its infancy. These charts were based on trial and error, as there was limited understanding of the relationship between X-ray exposure and image quality.
Over time, research and clinical experience led to the refinement of these charts, resulting in the standardized charts used today.
Key Components
An X-ray KVP and MAS chart typically consists of the following sections:
- Patient information:Includes the patient’s age, weight, and body part being examined.
- X-ray technique:Specifies the KVP and MAS settings for the examination.
- Image quality indicators:Provides guidance on the expected image quality, such as contrast and detail.
- Radiation dose information:Estimates the radiation dose to the patient based on the selected KVP and MAS settings.
Understanding KVP and MAS Parameters
Understanding the concepts of Kilovoltage Peak (KVP) and Milliampere Seconds (MAS) is essential for optimizing image quality in X-ray imaging. These parameters play a crucial role in determining the penetration and contrast of the X-ray beam, thereby affecting the visibility and diagnostic value of the resulting image.
Kilovoltage Peak (KVP)
Kilovoltage Peak (KVP) represents the maximum energy of the X-ray beam generated by the X-ray tube. It is measured in kilovolts (kV) and directly influences the penetrating power of the beam. Higher KVP values result in X-rays with greater energy and penetration, allowing them to pass through denser tissues and structures.
Milliampere Seconds (MAS)
Milliampere Seconds (MAS) measures the amount of electrical current flowing through the X-ray tube over a specific time. It determines the quantity of X-rays produced and affects the overall intensity of the beam. Higher MAS values result in a greater number of X-rays being generated, leading to increased beam intensity and shorter exposure times.
Relationship between KVP and MAS
The relationship between KVP and MAS is inversely proportional. Increasing KVP while maintaining the same MAS will reduce the beam intensity, while decreasing KVP will increase the intensity. Conversely, increasing MAS while maintaining the same KVP will increase the beam intensity, while decreasing MAS will reduce it.
Understanding the interplay between KVP and MAS is crucial for optimizing image quality. By adjusting these parameters, radiographers can control the penetration and contrast of the X-ray beam, ensuring that the resulting image provides the necessary diagnostic information.
Factors Influencing KVP and MAS Selection
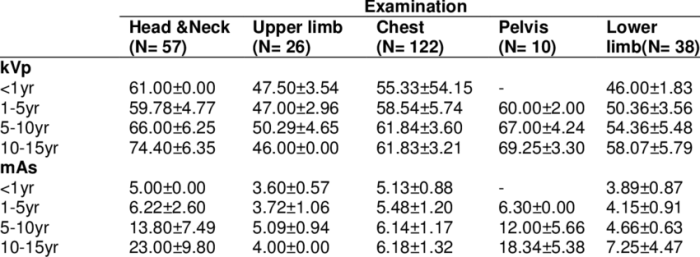
Selecting appropriate KVP and MAS settings is crucial for optimizing image quality and minimizing patient exposure during X-ray examinations. Several factors influence the choice of these parameters, including:
Patient Factors
-
-*Patient size and thickness
Larger patients require higher KVP to penetrate thicker tissues.
-*Density of the body part
Denser structures, such as bones, require higher KVP to penetrate.
-*Patient age
Children and infants have more sensitive tissues and require lower KVP and MAS settings.
Imaging Objectives
-
-*Diagnostic task
Different imaging tasks, such as visualizing soft tissue or bone, require different KVP and MAS settings.
-*Image quality requirements
Higher KVP and MAS settings generally result in better image quality, but may increase patient exposure.
Equipment Factors
-
-*X-ray tube
The type and condition of the X-ray tube can affect the optimal KVP and MAS settings.
-*Detector type
Different detectors, such as film-screen cassettes or digital detectors, have varying sensitivities and require different KVP and MAS settings.
Balancing Considerations
Optimizing KVP and MAS settings involves balancing the need for adequate image quality with the goal of minimizing patient exposure. Higher KVP and MAS settings penetrate deeper and provide better image quality, but increase patient exposure. Conversely, lower KVP and MAS settings reduce patient exposure but may compromise image quality.
Examples of KVP and MAS Settings
The following table provides examples of KVP and MAS settings for different body parts and imaging scenarios:| Body Part | Imaging Task | KVP | MAS ||—|—|—|—|| Chest | PA view | 120 | 10 || Abdomen | AP view | 80 | 15 || Skull | Lateral view | 70 | 5 || Spine | AP view | 100 | 20 |
Practical Applications of KVP and MAS Charts
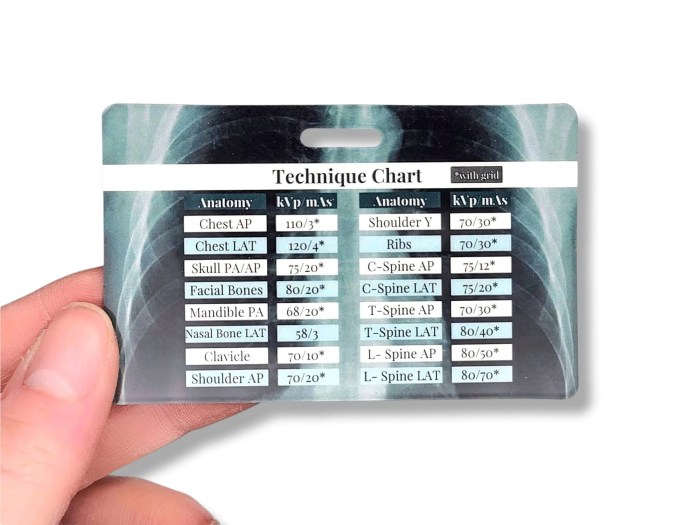
X-ray KVP and MAS charts serve as invaluable tools for radiographers, enabling them to determine optimal exposure settings for various imaging examinations. These charts provide a systematic approach to selecting appropriate KVP and MAS values based on the patient’s anatomy and the desired image quality.
Understanding how to use an X-ray KVP and MAS chart is essential for ensuring accurate and safe radiographic examinations. This guide will provide a step-by-step approach to using the chart effectively and highlight the consequences of using incorrect settings.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using an X-ray KVP and MAS Chart
- Identify the patient’s anatomy and the desired image quality.
- Locate the corresponding section of the chart based on the patient’s anatomy (e.g., chest, abdomen, extremities).
- Find the appropriate KVP range for the desired image quality (e.g., high contrast, low noise).
- Select a specific KVP value within the range that is suitable for the patient’s anatomy and the desired image quality.
- Determine the corresponding MAS value based on the selected KVP value and the patient’s anatomy.
It is crucial to adhere to the recommended KVP and MAS values provided by the chart. Using incorrect settings can compromise image quality, resulting in overexposure or underexposure, and potentially harming the patient. Overexposure increases the patient’s radiation dose and can lead to skin damage, while underexposure may result in insufficient image detail and necessitate retakes, further exposing the patient to radiation.
Advanced Considerations and Techniques
Optimizing image quality using KVP and MAS involves advanced techniques that enhance image clarity and reduce artifacts. These techniques include automatic exposure control (AEC), scatter reduction, and image processing algorithms.
X-ray KVP and MAS charts are essential tools for medical professionals. These charts help determine the appropriate settings for X-ray machines to ensure optimal image quality and patient safety. For those looking to expand their knowledge beyond medical imaging, the Wordly Wise Book 2 PDF offers a comprehensive guide to vocabulary development.
Returning to the topic of X-ray KVP and MAS charts, understanding these parameters is crucial for obtaining accurate and diagnostic images.
Automatic Exposure Control (AEC), X ray kvp and mas chart
AEC is a feature in modern X-ray systems that automatically adjusts KVP and MAS based on the patient’s anatomy. It ensures optimal exposure for different body parts, reducing the risk of over- or under-exposure. AEC provides consistent image quality, minimizes repeat exposures, and reduces radiation dose.
Scatter Reduction Techniques
Scatter is a phenomenon that degrades image quality by creating unwanted radiation that originates from outside the region of interest. Scatter can be minimized using various techniques:
- Grids:Lead or plastic grids absorb scattered radiation, improving image contrast and reducing noise.
- Anti-scatter cassettes:These cassettes contain a layer of material that absorbs scattered radiation, enhancing image clarity.
- Collimation:Limiting the X-ray beam to the area of interest reduces scatter from surrounding tissues.
Troubleshooting and Error Handling: X Ray Kvp And Mas Chart
Understanding and correctly using X-ray KVP and MAS charts are essential for obtaining optimal image quality and minimizing radiation exposure. However, it’s not uncommon to encounter errors or pitfalls while working with these charts. Identifying and addressing these issues is crucial for ensuring accurate and safe X-ray examinations.
Common Errors and Pitfalls
- Incorrect KVP or MAS Selection:Misinterpreting the chart or failing to consider patient factors can lead to incorrect exposure settings, resulting in over- or under-exposure.
- Equipment Malfunction:Faulty X-ray equipment or improper calibration can provide inaccurate readings, affecting exposure settings.
- Human Error:Mistakes in reading or applying the chart can lead to incorrect exposure settings.
Troubleshooting and Resolution
To resolve issues related to incorrect exposure settings, the following steps can be taken:
- Verify Equipment Calibration:Ensure that the X-ray equipment is properly calibrated and functioning correctly.
- Review Patient Information:Consider the patient’s size, thickness, and any anatomical variations that may affect exposure settings.
- Re-check the Chart:Carefully review the X-ray KVP and MAS chart to ensure the correct settings are selected for the specific examination.
- Seek Expert Advice:If troubleshooting efforts fail, consult with a qualified medical physicist or radiologist for assistance.
Importance of Quality Control
Regular quality control and monitoring of X-ray equipment are vital for ensuring the accuracy and safety of X-ray examinations. This includes:
- Regular Equipment Inspections:Inspecting X-ray equipment regularly to identify any potential issues or malfunctions.
- Calibration Checks:Performing calibration checks to ensure that the equipment is providing accurate readings.
- Image Quality Monitoring:Evaluating the quality of X-ray images to identify any inconsistencies or deviations from expected results.
By implementing these quality control measures, healthcare providers can minimize the risk of errors and ensure that X-ray examinations are performed safely and effectively.
Helpful Answers
What is the purpose of an X-ray KVP and MAS chart?
X-ray KVP and MAS charts guide radiographers in selecting appropriate exposure settings to optimize image quality and minimize patient exposure.
How do KVP and MAS affect image quality?
KVP influences image penetration, while MAS determines image density. Adjusting these parameters allows radiographers to tailor images to specific anatomical regions and imaging objectives.
What factors influence KVP and MAS selection?
Patient size, body part being imaged, and desired image quality are key factors that influence the selection of KVP and MAS settings.